Table of Contents

Bangladesh | Home of Natural beauty
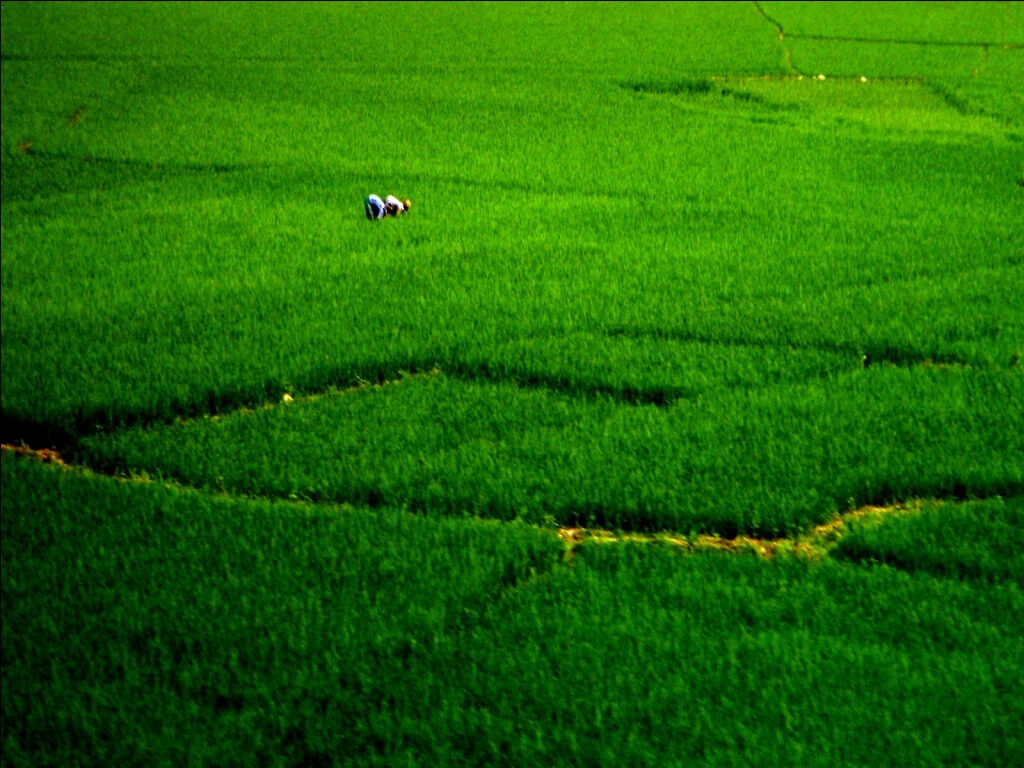
Bangladesh is a South Asian country located on the Bay of Bengal, sharing borders with India to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar (Burma) to the southeast. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with over 160 million people, and the capital city is Dhaka.
Key Facts about Bangladesh:

Geography:
- The country is known for its vast river systems, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers.
- Bangladesh is low-lying and prone to flooding, particularly during the monsoon season.
- The Sundarbans mangrove forest, home to the Bengal tiger, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

History:
- Bangladesh was part of British India until 1947, after which it became East Pakistan following the partition of India.
- In 1971, after a war of independence, it became an independent country, separating from Pakistan.
Economy:
- Bangladesh has a growing economy, with the ready-made garment industry being one of its major drivers.
- Agriculture, especially rice, tea, and jute, also plays a crucial role in the country’s economy.
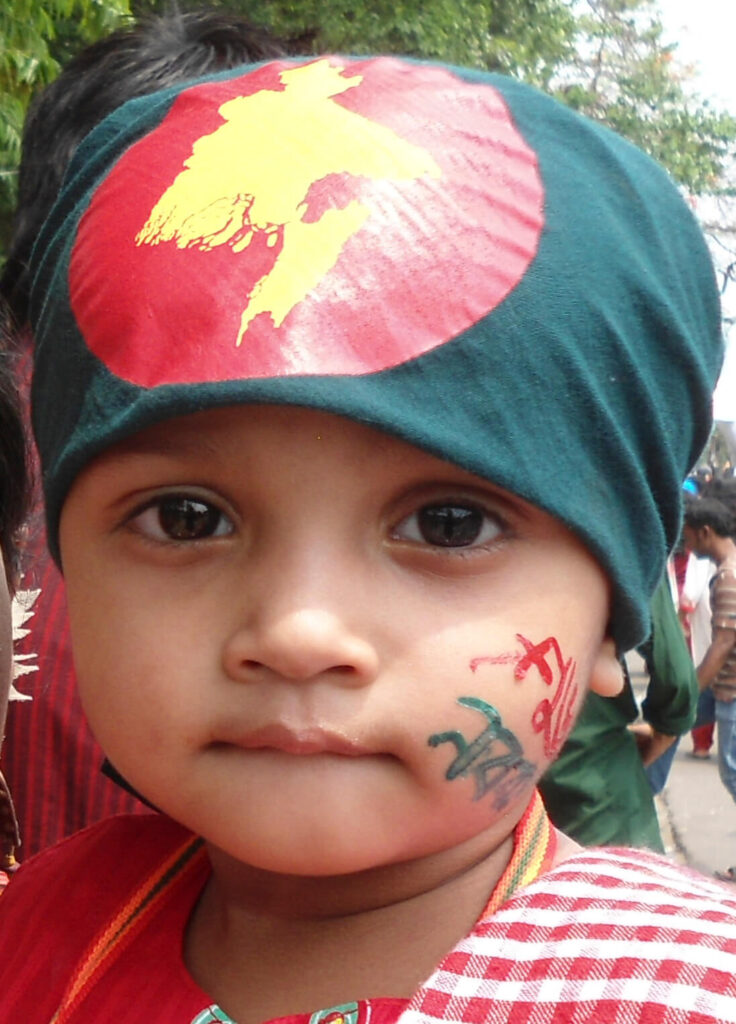

Culture:
- The predominant religion is Islam, followed by Other religion.
- Bengali is the official language, and the country has a rich literary and cultural tradition, with famous poets like Rabindranath Tagore and Kazi Nazrul Islam.
- Pahela Baishakh (Bengali New Year) is one of the most widely celebrated festivals.

Challenges:
- Bangladesh faces challenges related to climate change, population density, and poverty, though it has made significant progress in recent years in areas like education and healthcare.
Government:
- Bangladesh is a parliamentary democracy, with a President as the head of state and a Prime Minister as the head of government.
Divisions and Their Districts
Bangladesh is divided into 8 divisions, and each division comprises several districts. Here’s a brief overview of the divisions and their respective districts:
- Dhaka Division
Dhaka is the capital and the largest city of Bangladesh. The division includes the following districts:- Dhaka
- Faridpur
- Gazipur
- Gopalganj
- Kishoreganj
- Madaripur
- Manikganj
- Munshiganj
- Narayanganj
- Narsingdi
- Rajbari
- Shariatpur
- Tangail
- Chittagong (Chattogram) Division
Located in the southeast, this division is home to Bangladesh’s largest seaport in the city of Chittagong:- Bandarban
- Brahmanbaria
- Chandpur
- Chittagong
- Comilla (Cumilla)
- Cox’s Bazar
- Feni
- Khagrachari
- Lakshmipur
- Noakhali
- Rangamati
- Rajshahi Division
This division is known for its rich cultural history and agricultural output, particularly mangoes:- Bogra
- Chapainawabganj
- Joypurhat
- Naogaon
- Natore
- Pabna
- Rajshahi
- Sirajganj
- Khulna Division
Known for the Sundarbans, the world’s largest mangrove forest, Khulna is in the southwestern part of Bangladesh:- Bagerhat
- Chuadanga
- Jessore (Jashore)
- Jhenaidah
- Khulna
- Kushtia
- Magura
- Meherpur
- Narail
- Satkhira
- Sylhet Division
This is a key division with a large diaspora, especially in the UK, and it is known for tea gardens and hills:- Habiganj
- Moulvibazar
- Sunamganj
- Sylhet
- Barisal (Barishal) Division
This division lies in the south-central part of the country, surrounded by rivers and often referred to as the “Venice of the East”:- Barisal
- Bhola
- Jhalokathi
- Patuakhali
- Pirojpur
- Rangpur Division
This division is relatively new and is known for agriculture, particularly rice, potato, and wheat cultivation:- Dinajpur
- Gaibandha
- Kurigram
- Lalmonirhat
- Nilphamari
- Panchagarh
- Rangpur
- Thakurgaon
- Mymensingh Division
Created in 2015, Mymensingh is one of the newest divisions and has a significant agricultural base:- Jamalpur
- Mymensingh
- Netrokona
- Sherpur
Administration of Districts
Each district is headed by a Deputy Commissioner (DC), an official who is responsible for administration, development, and law enforcement within the district. Districts are divided into upazilas or sub-districts, each of which is administered by an Upazila Nirbahi Officer (UNO).
These districts serve as important administrative, cultural, and economic hubs within their respective divisions. Each district also plays a significant role in local governance, agricultural production, and regional trade.